The limitations of singly linked lists
The singly linked list (SLL) is a linear data structure comprising of nodes chained together in a single direction. Each node contains a data member holding useful information, and a pointer to the next node.
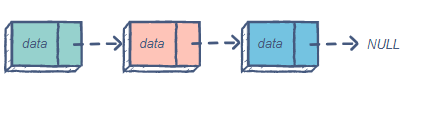
The problem with this structure is that it only allows us to traverse forward, i.e., we cannot iterate back to a previous node if required.
The doubly linked list class
From the definition above, we can see that a DLL node has three fundamental members:
- the data
- a pointer to the next node
- a pointer to the previous node
Struct node{
int data;
struct node *next, *prev;
*head;
Time Complexity
The worst case complexity for search, insertion, and deletion is O(n). Insertion and deletion at the head can be done in O(1).